S p d f orbitals chart 259927-What are s p d f orbitals
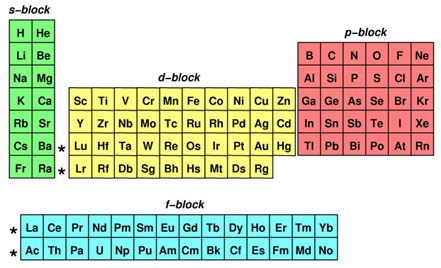
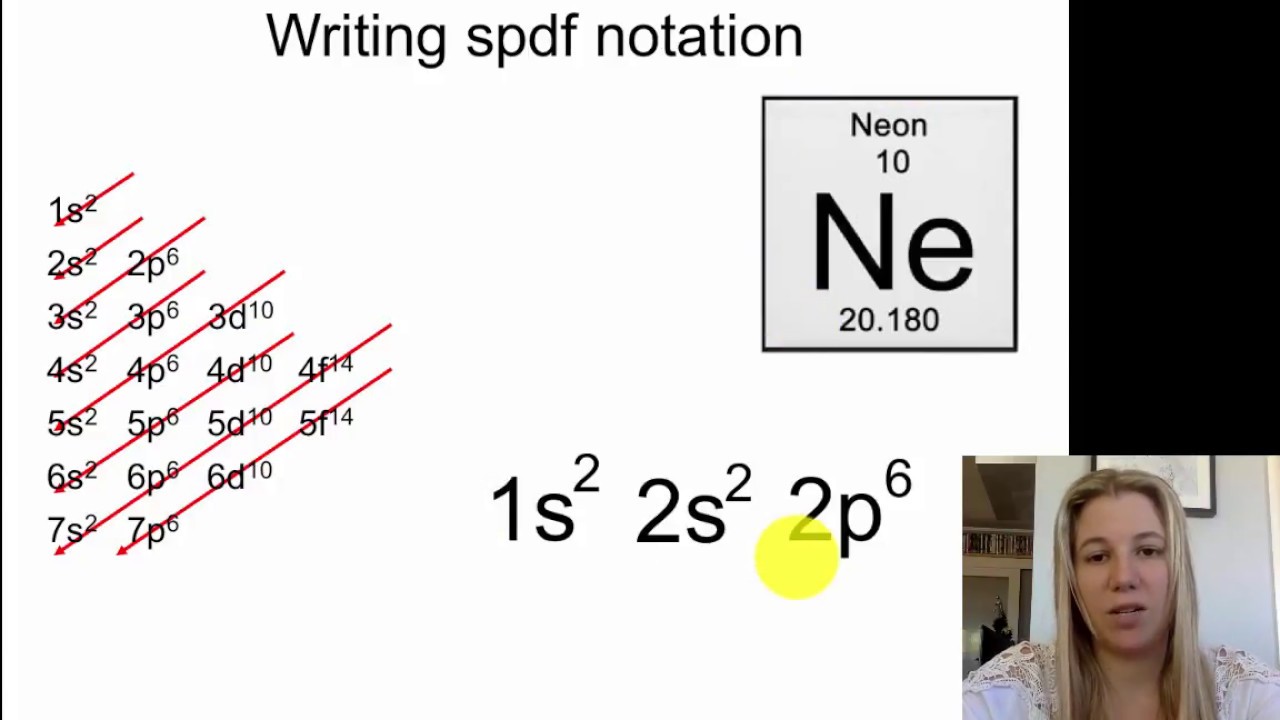
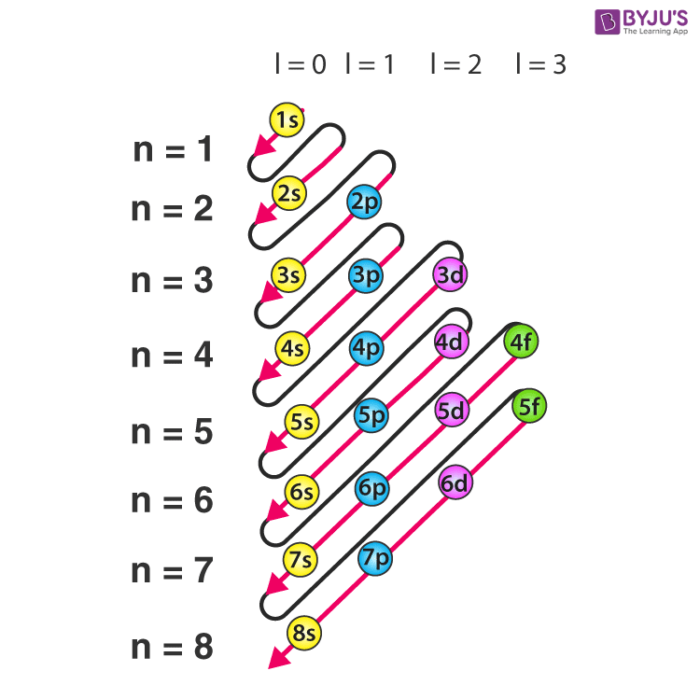
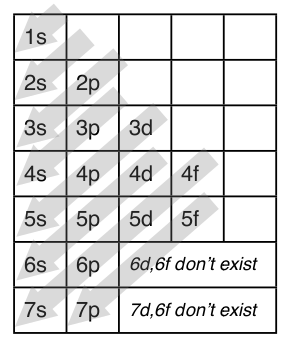
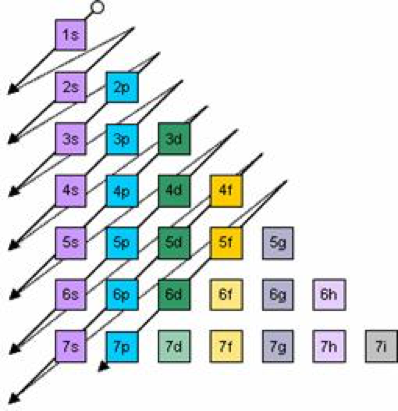
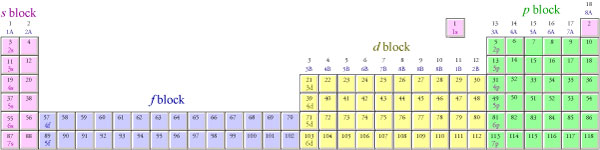
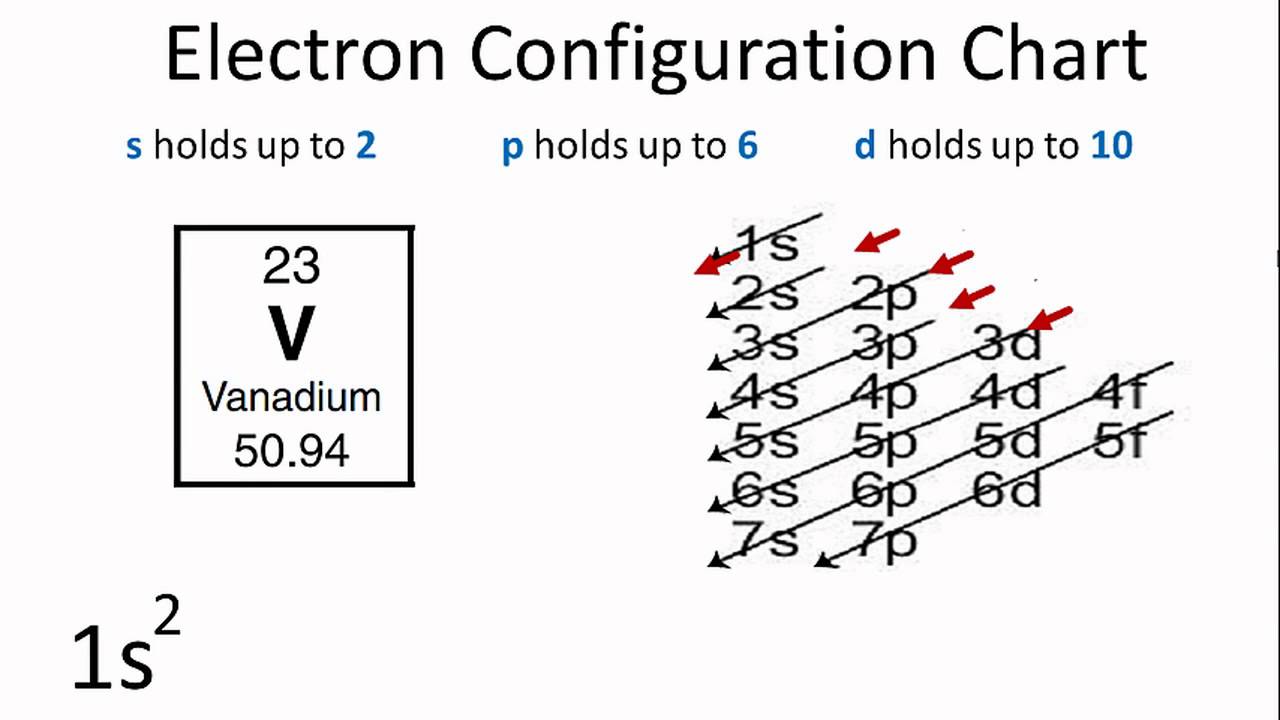
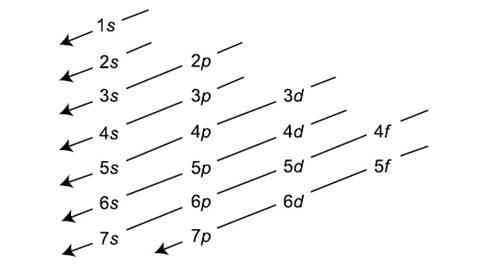
1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d, 5p, 6s, 4f, 5d, 6p, 7s, 5f s can hold 2 electrons p can hold 6 electrons d can hold 10 electrons f can hold 14 electrons Note that individual orbitals hold a maximum of two electrons There can be two electrons within an s orbital, p orbital, or d orbitalEach of these subshells (s, p, d and f) can hold specific maximum numbers of electrons s = 2, p = 6, d = 10, and f = 14 These subshells are further divided into orbitalsThe periodic table shows us the sequential filling of the electrons The energy of the orbitals determines the sequence of filling Lower energy orbitals are always preferred over high energy onesThe table is thus divided into 4 blocks namely – s,p,d, f blocks, depending on the occupation of the respective orbitals by the valence electrons
Electron Configuration Texas Gateway
What are s p d f orbitals
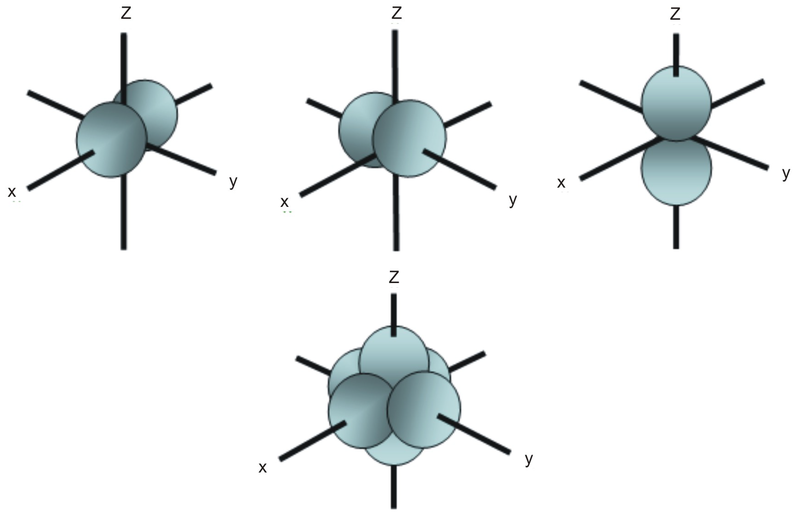
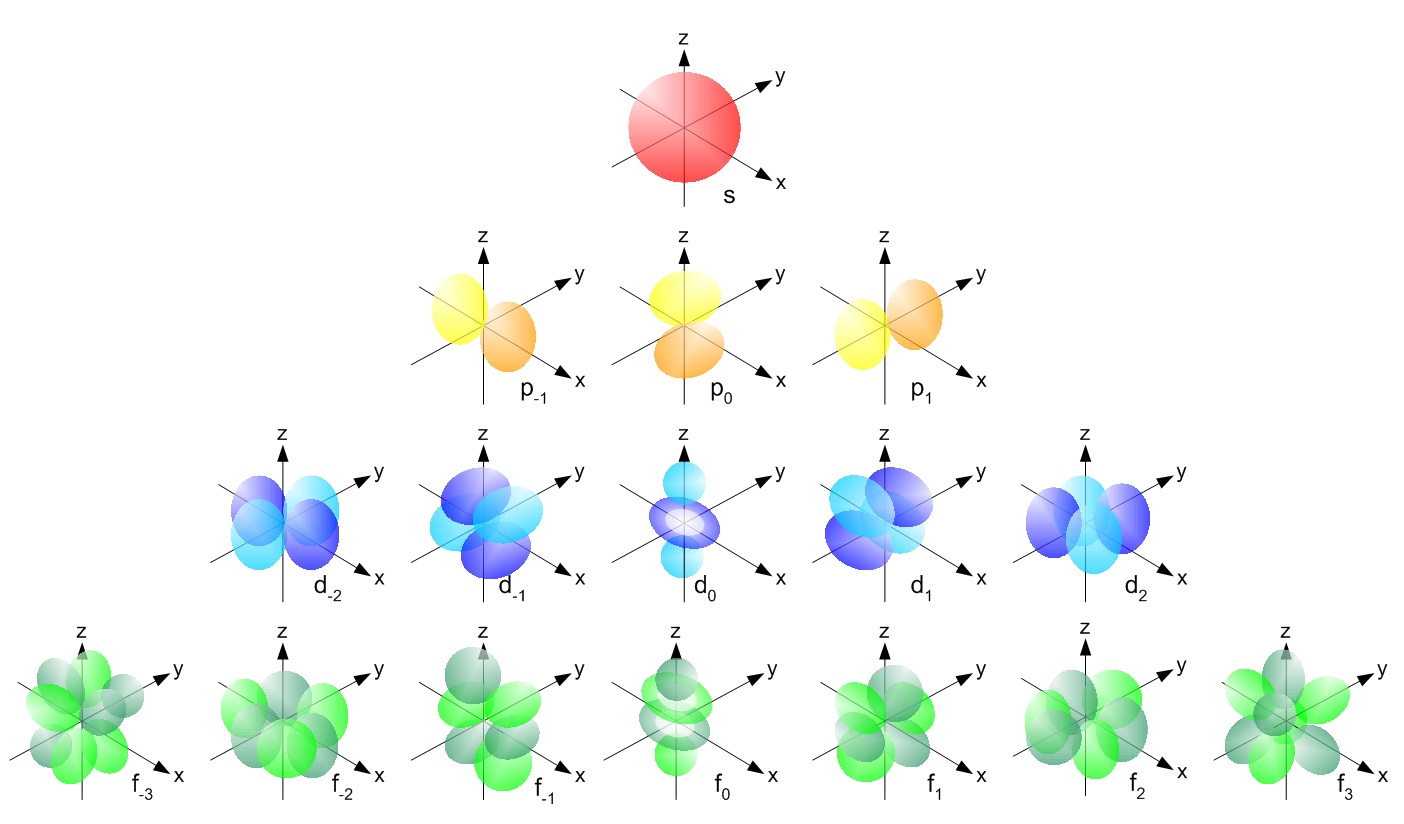
What are s p d f orbitals-The s, p, and d orbitals are quite familiar to anyone who has studied the electronic structure of atoms The forbitals, on the other hand, are not so familiar Interestingly, while the s, p, and d orbitals are presented as singular sets, there are two (2) sets in common usage for the forbitals cubic and general 1"s" subshell One possible orientation "p" subshell Three possible orientations There are five possible orbitals in a "d" subshell, and 7 possible orbitals in an "f" subshell!



Bromine Electron Configuration Br With Orbital Diagram
Maximum 6 electrons in 3 orbitals Maximum 2 electrons in 1 orbital Maximum 10 electrons in 5 orbitals Maximum 14 electrons in 7 orbitalsThe s orbital, p orbital, d orbital, and f orbital refer to orbitals that have an angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2, and 3, respectively The letters s, p, d, and f come from the descriptions of alkali metal spectroscopy lines as appearing sharp, principal, diffuse, or fundamentalAn electron in a p orbital has equal probability of being in either half The shapes of the other orbitals are more complicated The letters s, p, d, f, originally were used to classify spectra descriptively into series called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental, before the relation between spectra and atomic electron configuration was
S&P 500 PE Ratio chart, historic, and current data Current S&P 500 PE Ratio is 3946, a change of 055 from previous market closeTutorial on s,p,d,f orbitals picture of periodic table with d block what is the 2p block periodic table why there are three 8b elements in periodic table show images of periodic table showing mass and atomic numbers periodic table visual basic pblock elementstutorial "pblock" chemistrytutorial The four main blocks of the table (s, p, d, andThe letters s, p, d,or f Levels and Sublevels 1 1 s 2 s p 3 s p d 4 s p d f 5 s p d f 6 s p d f 7 s p d f You can see that the innermost zone, level 1, contains only one sublevel, s Level 2 contains sublevels s and p Level 4 is the first level that can contain all four sublevelss, p, d,and f
"s" subshell One possible orientation "p" subshell Three possible orientations There are five possible orbitals in a "d" subshell, and 7 possible orbitals in an "f" subshell!Each letter (s, p, d, f) corresponds to a particular orbital (sometimes called subshell) 1s refers to the s orbital on the first shell, 3p refers to the p orbital on the 3rd shell, etc Each orbital (s, p, d, f) has a number associated with it, called its azimuthal quantum number, sometimes referred to as ℓ This number describes the shapeThese are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one node



The Parts Of The Periodic Table


Electron Configuration Spdf Notation Part 2 Youtube
S P D F Orbitals Teaching Chemistry Hilbert Spherical Harmonics Orbitals Basics Atomic Orbital Tutorial Probability Shapes Energy Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Experiments A Chart Of The Spdf Electron Orbitals Chemistry Education Chemistry Lessons Chemistry LabsThe p orbital set contains 3 orbitals, and thus can hold a total of 6 electrons The d orbital set contains 5 orbitals, so it can hold 10 electrons The f orbital set contains 7 orbitals, so it can hold 14 electrons The g, h, i and k orbital sets are theoretical No known atoms have electrons in any of these orbitalsAn electron in a p orbital has equal probability of being in either half The shapes of the other orbitals are more complicated The letters s, p, d, f, originally were used to classify spectra descriptively into series called sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental, before the relation between spectra and atomic electron configuration was
/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)


Electron Configuration Chart


Electron Configuration Detailed Explanation With Examples
Now, you'll also hear the term, subshell, subshell, or sometimes people will say sublevels and that's where they're talking about s or p or d and eventually f so if I circle this, I'm talking about that first shell Now, the first shell only contains one subshell and that's the 1s subshell and the 1s subshell only has one orbitalLetter s p d f g h The subshell with n=2 and l=1 is the 2p subshell;D and f orbitals In addition to s and p orbitals, there are two other sets of orbitals that become available for electrons to inhabit at higher energy levels At the third level, there is a set of five d orbitals (with complicated shapes and names) as well as the 3s and 3p orbitals (3p x, 3p y, 3p z) At the third level there are nine total
/ecblocks-56a129535f9b58b7d0bc9f2e.jpg)


What Are Element Blocks On The Periodic Table


What Is The Electron Configuration For Francium Socratic
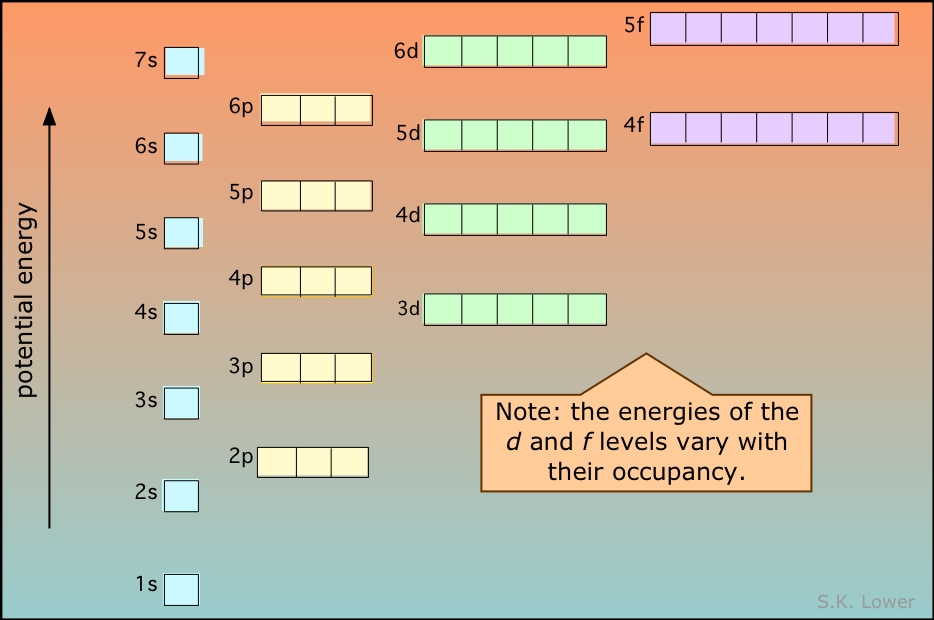
2s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,If n=3 and l=0, it is the 3s subshell, and so Thus the s subshell has only one orbital, the p subshell has three orbitals, and so on 4 Spin Quantum Number (m s) m s = ½ or ½ Specifies the orientation of the spin axis of an electron An electron can spin inSubshells are labelled s, p, d, and f in an electron configuration Subshell Examples Here is a chart of subshells, their names, and the number of electrons they can hold Subshell S P D F Orbitals and Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers Pauli Exclusion Principle Definition


Spdf Drone Fest



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange
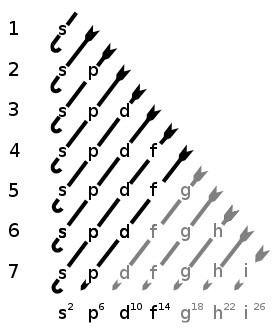
2 refers to the next energy level further out, and so on The letter refers to the shape of the orbital The letters go in the order s, p, d, f, g, h, i, j, etc The letters s, p, d, and f were assigned for historical reasons that need not concern usSub Shells and Orbitals This model can be further refined by the concept of sub shells and orbitals Sub shells are known by letters s, p, d, and f The s sub shell can contain 2 electrons, p 6, d 10 and f 14 Electrons occupy negative charge clouds called orbitals, each orbital can hold only 2 electronsHybridization Involving d Orbitals Atoms in the third period and higher can utilize d orbitals to form hybrid orbitals PF 5 Similarly hybridizing one s, three p and two d orbitals yields six identical hybrid sp 3 d 2 orbitals These would be oriented in an octahedral geometry


What Is The Correct Electron Configuration For Uranium Quora


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding
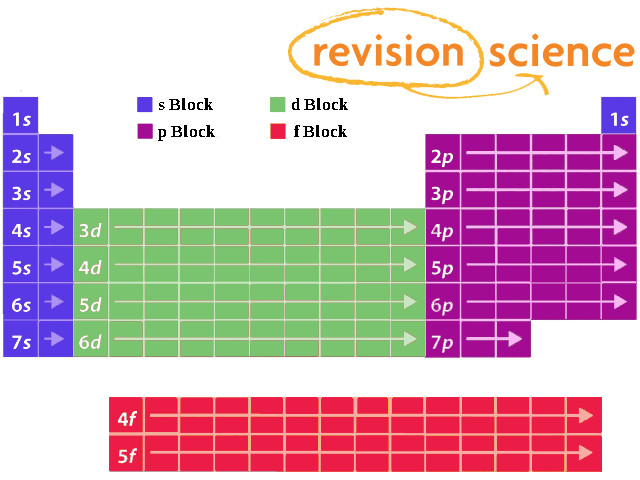
P Orbitals Only s orbitals are spherically symmetrical As the value of l increases, the number of orbitals in a given subshell increases, and the shapes of the orbitals become more complex Because the 2p subshell has l = 1, with three values of m l (−1, 0, and 1), there are three 2p orbitals Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\), the colors correspond to regions of space where the phase of the waveS block first 2 columns on the left hand side of the Periodic Table d block 10 columns in the middle of the Periodic Table p block last 6 columns on the right hand side of the Periodic Table f block bottom 2 rows separated from the rest of the Periodic Table Period 1Sublevel Name s p d f Number of Orbitals 1 3 5 7 Maximum number of electrons 2 6 10 14 4 Each sublevel has increasing odd numbers of orbitals available s = 1, p = 3, d = 5, f = 7 Each orbital can hold only two electrons and they must be of opposite spin An ssublevel holds 2 electrons, a psublevel holds 6 electrons, a dsublevel holds 10



Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


The Electron Configurations Of Atoms The Electron Configuration Of An Atom Shows The Number Of Electrons In Each Sublevel In Each Energy Level Of The Ground State Atom To Determine The Electron Configuration Of A Particular Atom Start At The Nucleus And
Tutorial on s,p,d,f orbitals picture of periodic table with d block what is the 2p block periodic table why there are three 8b elements in periodic table show images of periodic table showing mass and atomic numbers periodic table visual basic pblock elementstutorial "pblock" chemistrytutorial The four main blocks of the table (s, p, d, andS, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;S P D F Orbitals Teaching Chemistry Hilbert Spherical Harmonics Orbitals Basics Atomic Orbital Tutorial Probability Shapes Energy Chemistry Lessons Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Experiments A Chart Of The Spdf Electron Orbitals Chemistry Education Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Labs


Chemistry Orbitals Chart The Future


Writing Electron Configurations Dummies
The maximum electrons that can be carried by the subshell S is 2, by P is 6, by D is 10, and the F subshell can carry 14 This decides the electron capacity of the shells The K shell contains a 1s subshell hence it can carry 2 electrons, the L shell has 2s and 2p, and can carry 8 electronsS, p, d, f and so on are the names given to the orbitals that hold the electrons in atoms These orbitals have different shapes (eg electron density distributions in space) and energies (eg 1s is lower energy than 2s which is lower energy than 3s;Explanation The proposed tetrahedral nucleus structure, along with rules for proton spin alignment that is the cause of the repelling force used to calculate orbital distances, can explain the shapes of the s, p, d and f orbitalsThe electron is always attracted to the atomic nucleus at any angle However, at certain angles, the alignment of oppositespin protons causes a change in the


1 4 Electron Configuration And Orbital Diagrams Chemistry Libretexts



S P D F Orbitals Explained 4 Quantum Numbers Electron Configuration Orbital Diagrams Youtube
The rest being named in alphabetical order from G onwards, except that J is omittedWhen used to describe electron states in an atom, the term symbol usually follows the electron configurationEach letter (s, p, d, f) corresponds to a particular orbital (sometimes called subshell) 1s refers to the s orbital on the first shell, 3p refers to the p orbital on the 3rd shell, etc Each orbital (s, p, d, f) has a number associated with it, called its azimuthal quantum number, sometimes referred to as ℓ This number describes the shapeL may have integer values from 0 to n–1 and corresponds to the sublevel orbitals s, p, d, f that have different shapes For n = 1, there is only one allowed value of l, l = o, representing an s orbital For n = 2, there are two allowed values of l, l = 0 (s orbital) and l = 1 (p orbital) The magnetic quantum number m (or m l


Q Tbn And9gcqgtf59q5s9i9gngbwkbd60z4tqcl Ckgqjpu0wd8l1itpdlpr3 Usqp Cau



Quantum Numbers N L Ml Ms Spdf Orbitals Youtube
The nomenclature (S, P, D, F) is derived from the characteristics of the spectroscopic lines corresponding to (s, p, d, f) orbitals sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental;The orbitals of a subshell are all equal For example, the p subshell has 3 orbitals All have the same energy Within an energy level, the s subshell is the lowest energy sublevel The f subshell is the highest energy sublevel The p & d sublevels are in the middle but d has more energy than pThus 1 refers to the energy level closest to the nucleus;
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


Electronic Structure And The Aufbau Principle



Solved Using Spdf Noble Gas Notation Write The Electron Chegg Com
These are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one nodeThese are s, p, d and f The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below sorbitals The sorbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus When n = 2 and l = 0 , ie 2s orbital which contains one nodeThis video explains s, p, d, and f orbitals, sublevels, and their shapes It discusses the 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms n represents the energy leve


Electron Configurations



Clarifying Electron Configurations Chemical Education Xchange
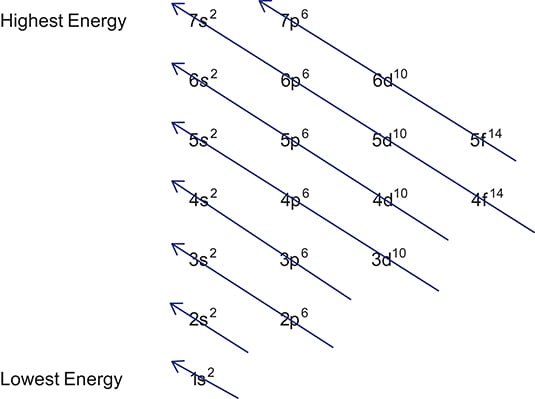
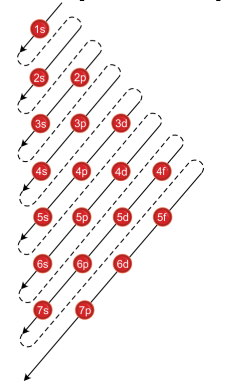
Add two electrons to each s sublevel, 6 to each p sublevel, 10 to each d sublevel, and 14 to each f sublevel To check your complete electron configuration, look to see whether the location of the last electron added corresponds to the element's position on the periodic table Predicting the Order of Filling of the OrbitalsThe repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d, and f atomic orbitals, respectively, although for higher values of the quantum number n, particularly when the atom in question bears a positive charge, the energies of certain subshells become very similar and so the order in which they are said to be populated by electrons (eg Cr = Ar4s 12s is lower energy than 2p)(image source)So for example,


Www Surryschools Net Cms Lib Va Centricity Domain 123 Electron Configuration Fall 16 Pdf


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
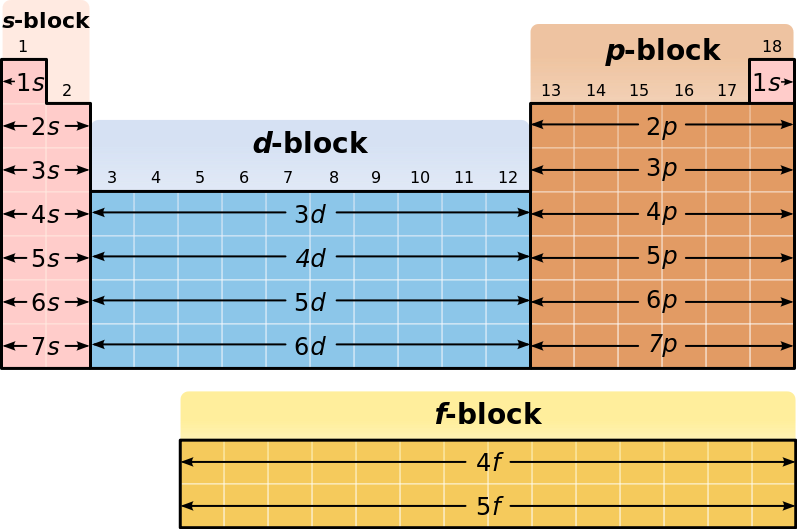
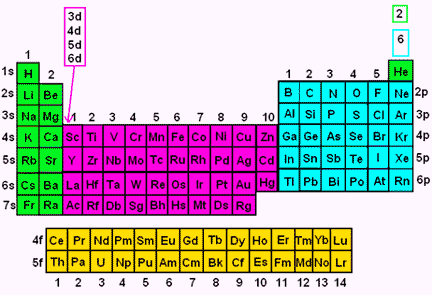
Elements in the long form of periodic table have been divided into four blocks ie s ,p ,d and f This division is based upon the name of the orbitals which receives the last electron S block elements 1)Elements in which the last electron enters the s orbital of their respective outermost shells are calledThe subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum s 1 orbital, 2 electrons p 3 orbitals, 6 electrons d 5 orbitals, 10 electrons f 7 orbitals, 14 electronsThe s, p, d, f and g are called atomic orbitals Filling up these orbitals with electrons builds atoms, and the way in which atoms are build up gives rise to the periodic table There is only one s orbital (m l = 0), but there are three p orbitals (m l = −1,0,1), five d orbitals (m



Bromine Electron Configuration Br With Orbital Diagram


Electron Configurations Orbitals Energy Levels And Ionisation Energy Trends A Level Chemistry Revision Notes
Maximum 6 electrons in 3 orbitals Maximum 2 electrons in 1 orbital Maximum 10 electrons in 5 orbitals Maximum 14 electrons in 7 orbitalsThis chart is straightforward to construct Simply make a column for all the s orbitals with each n shell on a separate row Repeat for p, d, and f Be sure to only include orbitals allowed by the quantum numbers (no 1p or 2d, and so forth) Finally, draw diagonal lines from top to bottom as shown 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 1 ExerciseThe subshells s, p, d, and f contain the following number of orbitals respectively, where every orbital can hold up to two electrons maximum s 1 orbital, 2 electrons p 3 orbitals, 6 electrons d 5 orbitals, 10 electrons f 7 orbitals, 14 electrons


An Atomic Model Our Present Model Of The Atom Is Based On The Concept Of Energy Levels For Electrons Within An Atom And On The Mathematical Interpretation Of Detailed Atomic Spectra The Requirements For Our Model Are Each Electron In A Particular Atom



Periodic Table Blocks Of Elements
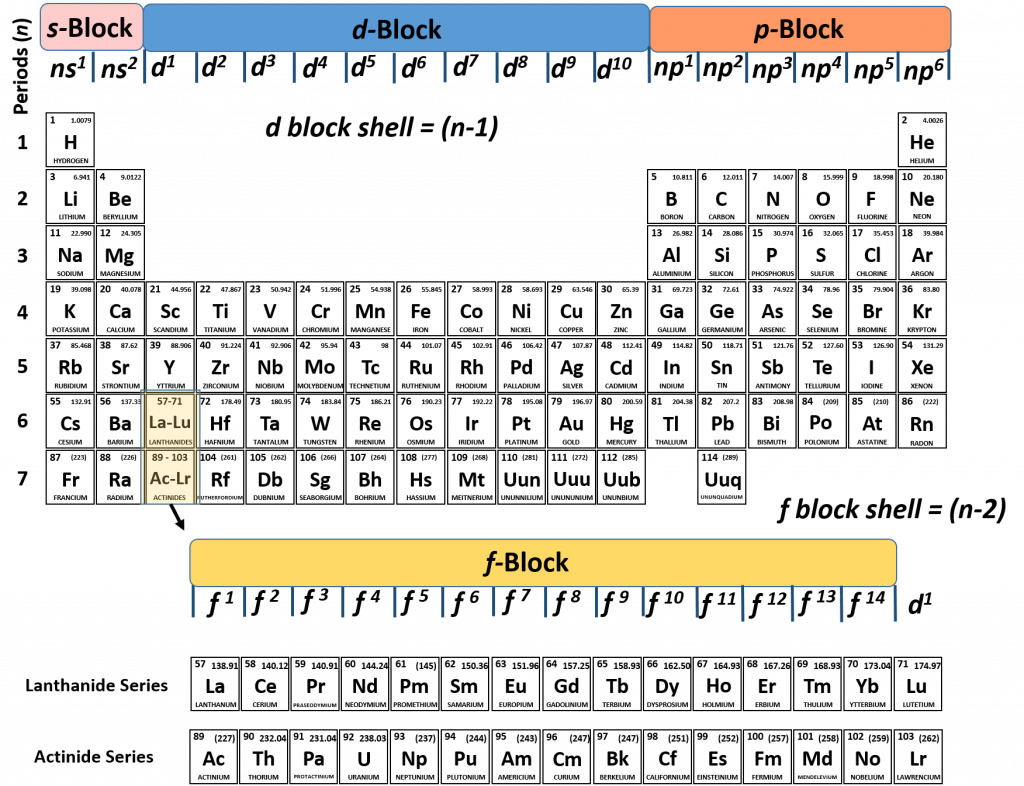
A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet Each block is named after its characteristic orbital sblock, pblock, dblock, and fblock The block names (s, p, d, and f) are derived from the spectroscopic notation for the value of an electron's azimuthal3D model to visualise the shapes of atomic orbitals s, p and dThe periodic table shows us the sequential filling of the electrons The energy of the orbitals determines the sequence of filling Lower energy orbitals are always preferred over high energy onesThe table is thus divided into 4 blocks namely – s,p,d, f blocks, depending on the occupation of the respective orbitals by the valence electrons



Orbitals Diagram For Spdf Quantum Numbers In High School Chemistry Physics And Mathematics Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry


Q Tbn And9gcsj4fgjpix3utxsz25hefqhut0jqwxk8hf0 Vlozplqv8ginn Usqp Cau


Electron Configurations



Electronic Structure Ppt Download



Solved 3 15 Review 1 2 Electrons The Chart Below Shows Chegg Com



Electron Configuration Texas Gateway


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Electron Configurations


Ch150 Chapter 2 Atoms And Periodic Table Chemistry
/4fz3-electron-orbital-117451436-587f69f23df78c17b6354ebd-f7499851032246f5bbe03f1ffba963d5.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



File Periodic Table Blocks Spdf 32 Column Svg Wikimedia Commons


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding



Valence Electron Definition Configuration Example Study Com Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Classroom Electron Configuration


Electron Configurations


Electron Configuration Wyzant Resources



7 3 Electron Configurations Of Atoms Chemistry Libretexts


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes


Electron Configuration Chemistry 10



A Chart Of The Spdf Electron Orbitals Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry



Atomic Orbitals 5 1 Continued Tutorial Sophia Learning


Using The Electron Configuration Chart Youtube


12 9 Orbital Shapes And Energies Chemistry Libretexts



Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model Chemistry Education Chemistry Classroom Teaching Chemistry


The Trouble With The Aufbau Principle Feature Rsc Education
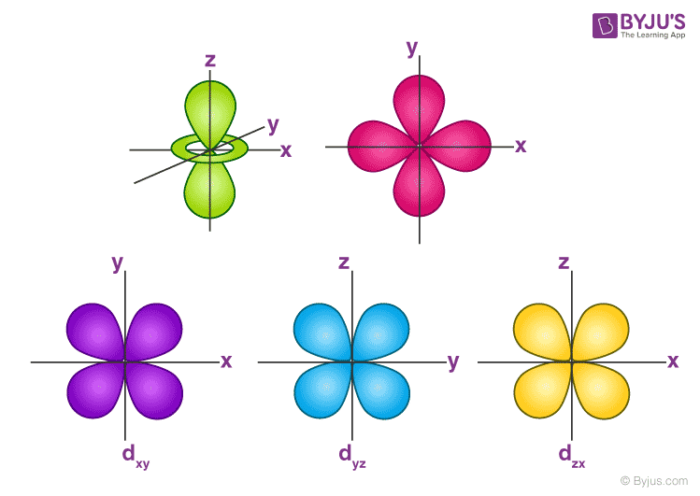


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital



Ppt S P D F Orbitals Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
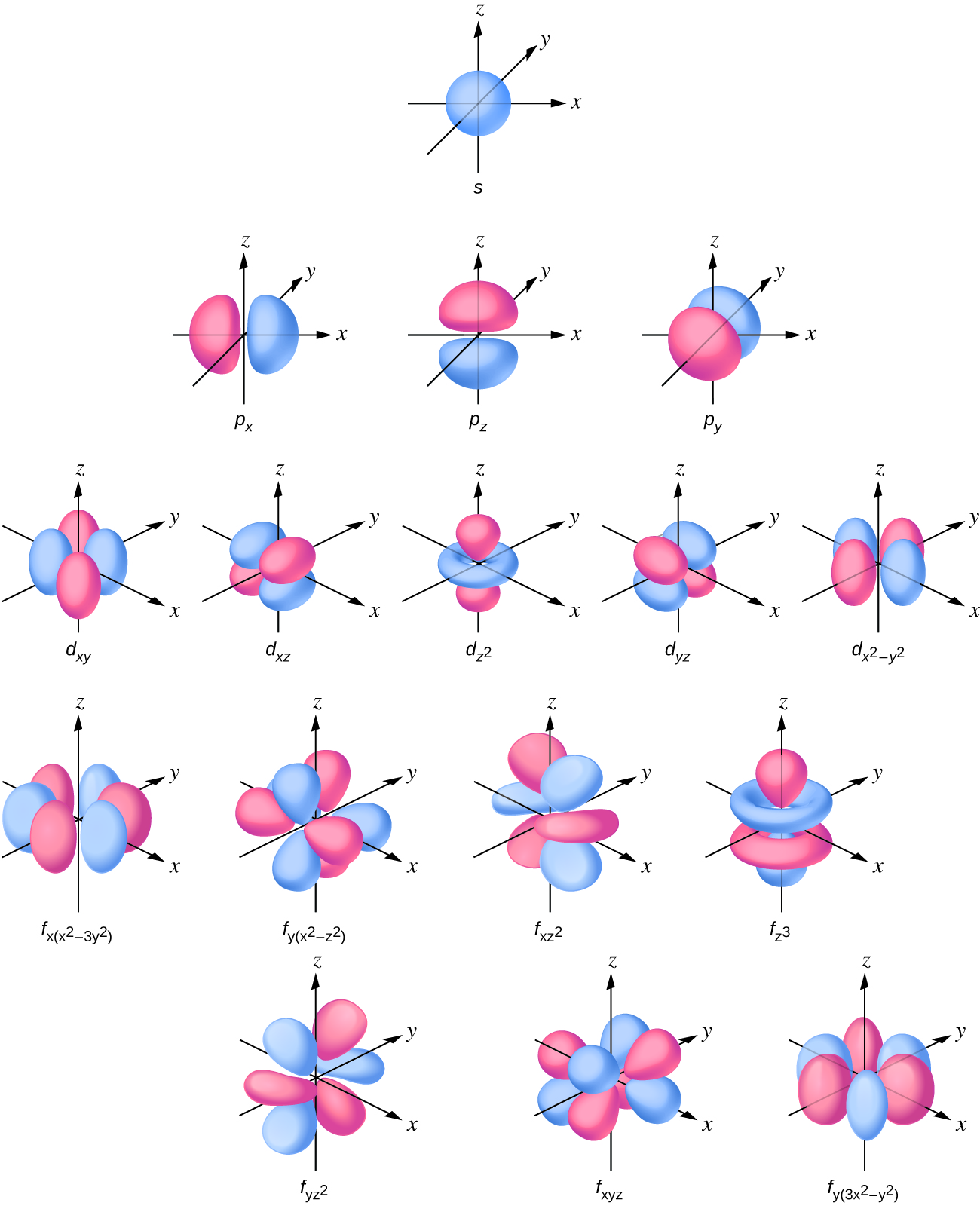


2 2 Atomic Orbitals And Quantum Numbers Chemistry Libretexts



What Is Spdf Configuration Chemistry Stack Exchange
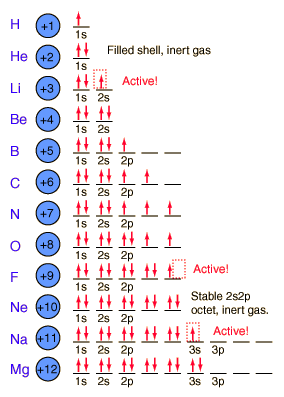


Orbitals


Orbitals And Electron Configuration


Vixra Org Pdf 1308 0130v1 Pdf



5 Steps Electron Configuration For Sulphur S In Just 5 Steps
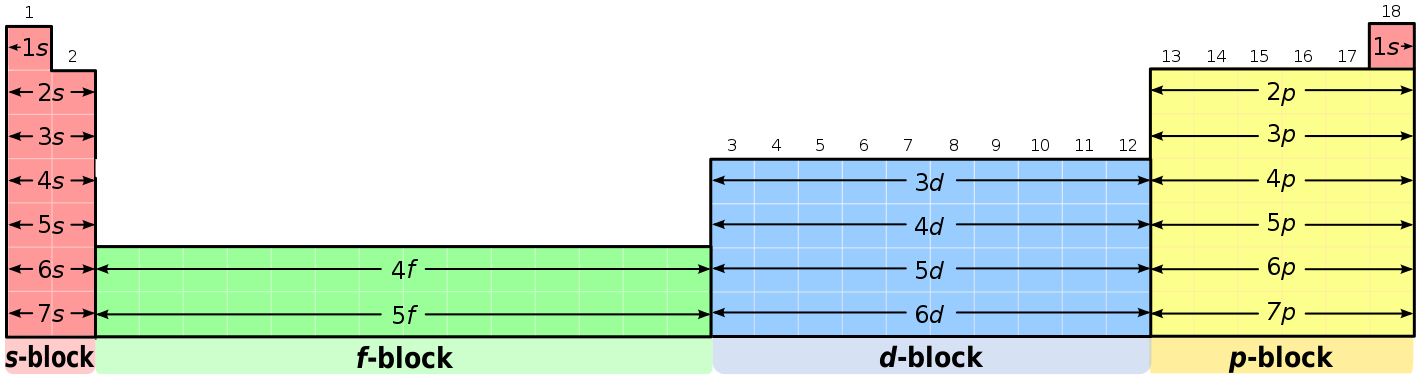


File Periodic Table Blocks Spdf 32 Column Svg Wikimedia Commons



Electron Configurations


Vixra Org Pdf 1308 0130v1 Pdf



Blocks Of The Periodic Table Chemistry For Non Majors
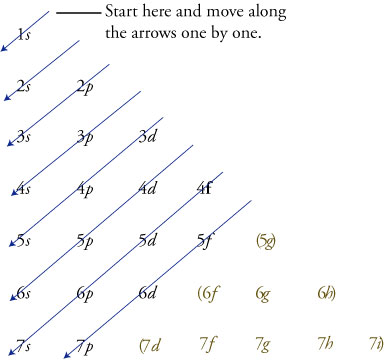


Electron Configurations


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding


Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes


S P D F Orbitals Chemistry Socratic
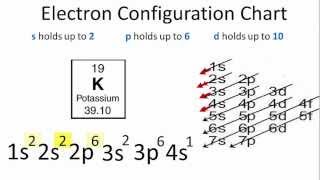


Electron Configuration For Potassium K
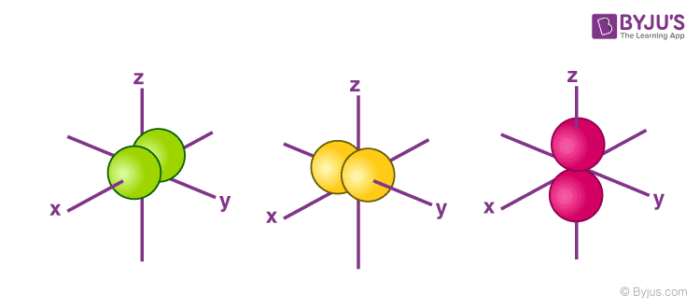


Orbitals Chemistry Shapes Of Atomic Orbitals Shape Of S P D And F Orbital
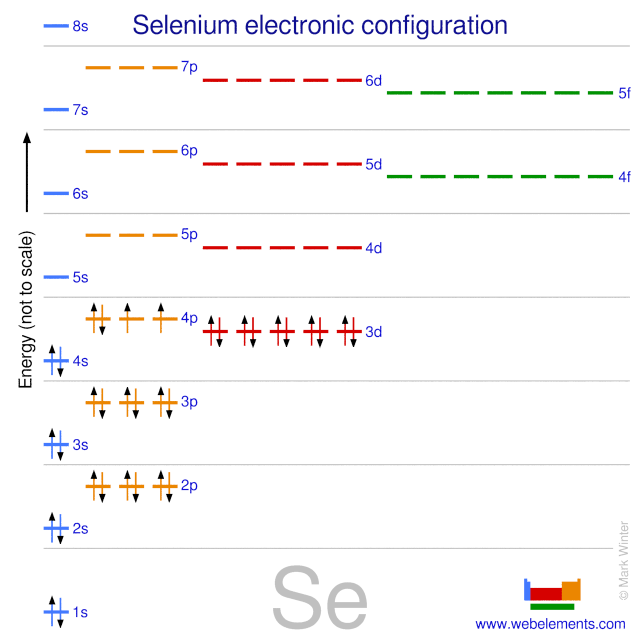


Webelements Periodic Table Selenium Properties Of Free Atoms



Electron Configuration Anomalies Villanova College Chemistry Blog
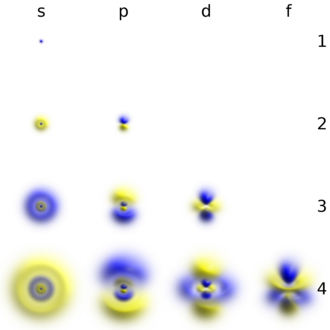


Electron Shell Wikipedia
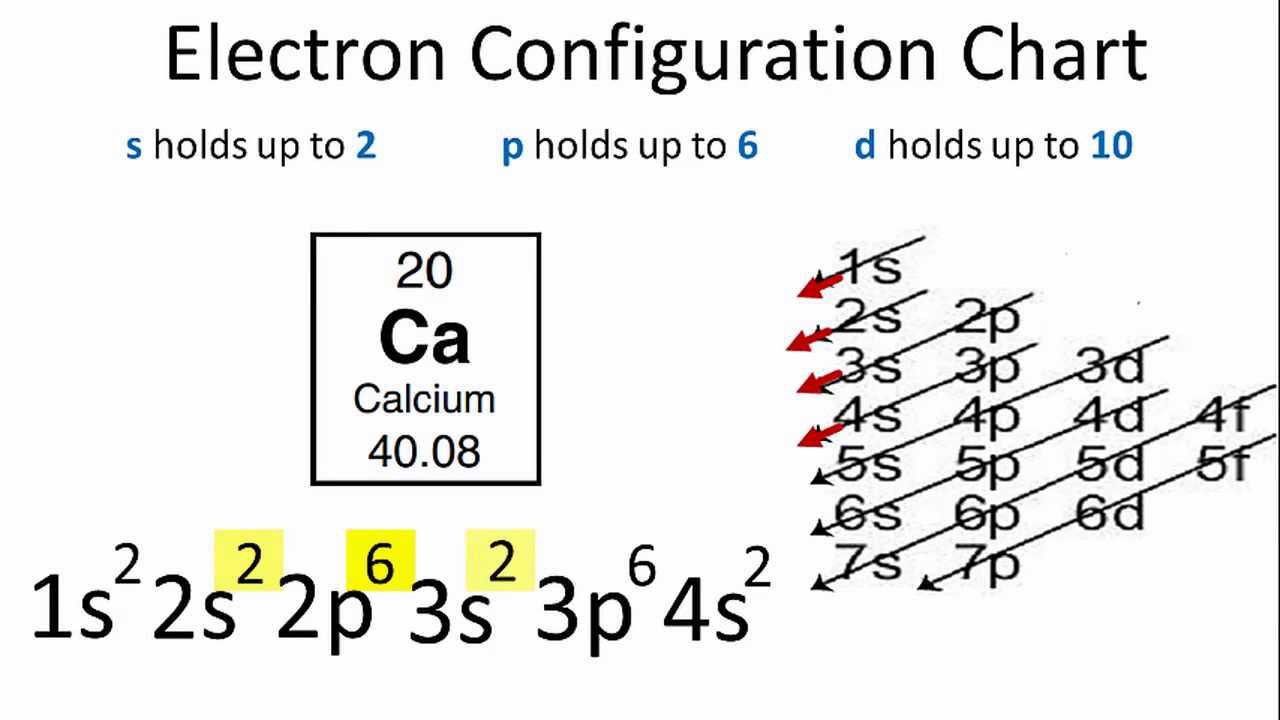


Electron Configuration For Calcium Ca


Electron Configurations A Must Know Hack


Vixra Org Pdf 1308 0130v1 Pdf


Q Tbn And9gcq8dvoj3blbzibn Pinxfr5zpqto 2 5yk28pboysmjqllqn0mr Usqp Cau
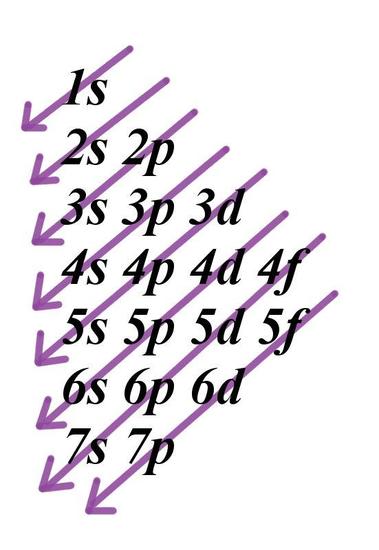


1 4 Electron Configurations Electronic Orbital Diagrams Review Chemistry Libretexts


Q Tbn And9gcth1rc3hbnde1titk095wzz5fdzyo5obndscg8azgis25 Lq4re Usqp Cau
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/energylevels-56a129545f9b58b7d0bc9f39-5aeb7f1aae9ab800373981a3.png)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers



Electron Configuration Wikipedia


Parsing Spdf Orbital Hybridization And Simple Bonding
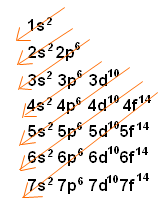


Electron Configuration Wyzant Resources
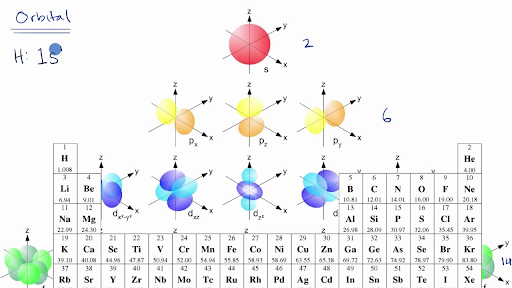


Introduction To Electron Configurations Video Khan Academy


Spdf Orbitals Chart Drone Fest



Iodine Electron Configuration I With Orbital Diagram


Vixra Org Pdf 1308 0130v1 Pdf



41 The Periodic Table S P D F Blocks Madoverchemistry Com


Atomic Orbitals
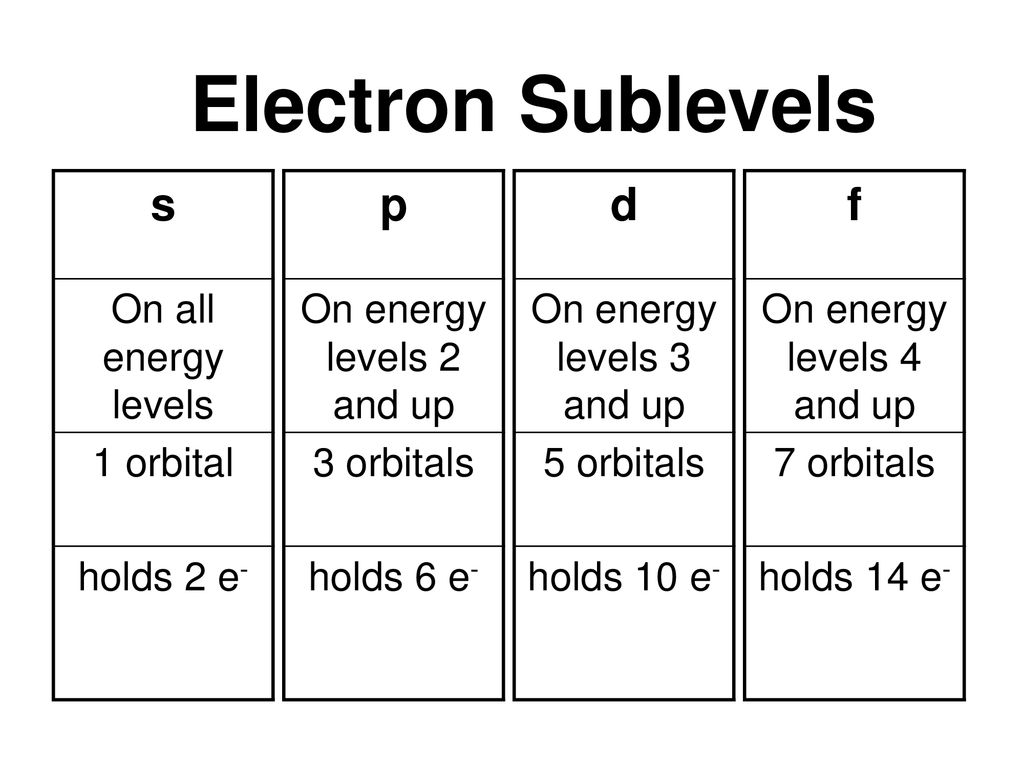


Sublevel Spdf Chart Fgkb Katasekan Site


Understanding The Bonding Of Second Period Diatomic Molecules


Parsing The Spdf Electron Orbital Model


Vixra Org Pdf 1308 0130v1 Pdf
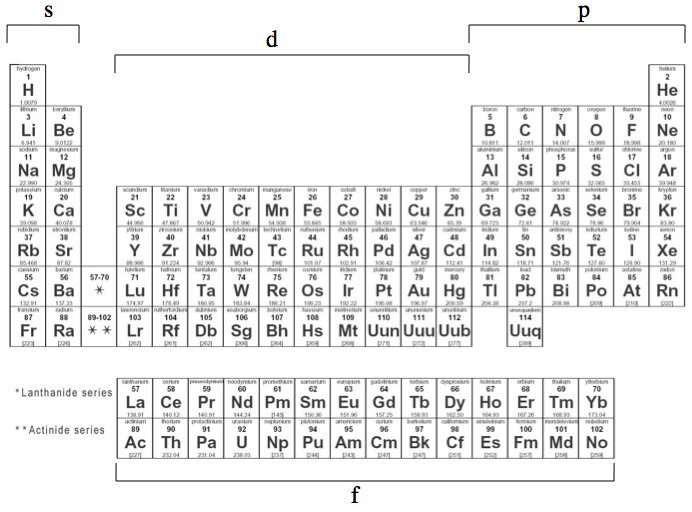


Q Is It Possible For An Atomic Orbital To Exist Beyond The S P F And D Orbitals They Taught About In School Like Could There Be A Other Letter Orbital Beyond


Vixra Org Pdf 1308 0130v1 Pdf



Electronic Configuration Of The D Block Elements Concepts Videos Q As
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aufbauexample-56a129555f9b58b7d0bc9f48.jpg)


S P D F Orbitals And Angular Momentum Quantum Numbers


Shells And Subshells A Level Chemistry



Chem 1 Mcat Flashcards Quizlet


How To Use Spdf Method For Electronic Configuration Chemistry Topperlearning Com 8ekub122


Q Is It Possible For An Atomic Orbital To Exist Beyond The S P F And D Orbitals They Taught About In School Like Could There Be A Other Letter Orbital Beyond



Quantum Mechanical Model Flashcards Quizlet


コメント
コメントを投稿